Overview
Uterine cancer happens when normal cells in the uterus change into abnormal cells and grow out of control. The uterus (also called the womb) is the part of a woman’s body that holds a baby if she is pregnant. The uterus has a thin inner lining layer and a thick outer layer.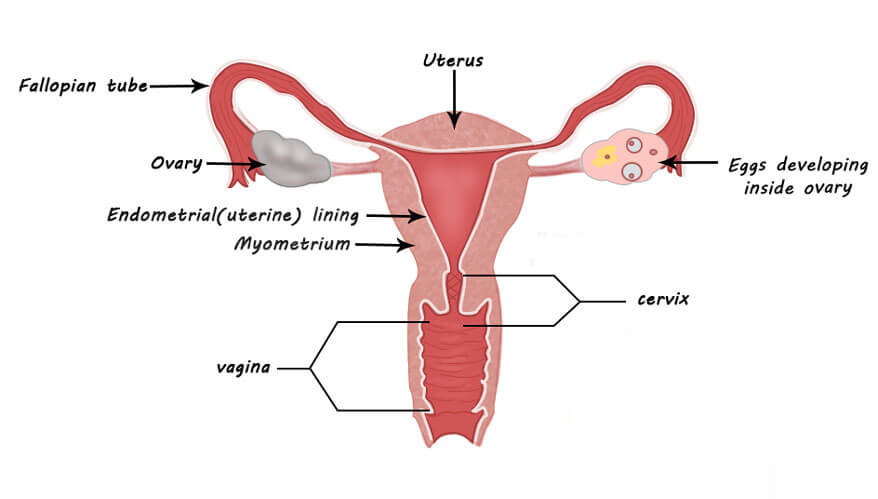
Female Genital Tract
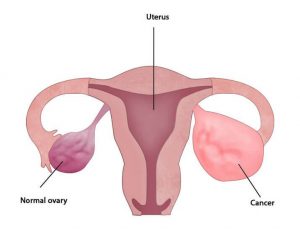
Uterine Cancer
There are different types of uterine cancer, but most uterine cancer starts in cells in the thin inner lining. Uterine cancer can occur in women of any age, but is much more common in women who have gone through menopause. Menopause is the time in a woman’s life when she stops having menstrual periods.
FAQs about Uterine cancer
The most common symptom of uterine cancer is abnormal vaginal bleeding. Abnormal vaginal bleeding includes:
- Bleeding in between menstrual cycles (at times other than during your period)
- Menstrual bleeding that is heavier than usual
- Any vaginal bleeding in a woman who has already gone through menopause
- Pain in lower abdomen
- Difficulty in urination
These symptoms can be caused by conditions that are not cancer. But if you have these symptoms, tell your doctor.
USG Abdomen
Sonography will tell about any abnormality in uterus. This test measures how thick the uterine lining is.
Biopsy
During a biopsy, a doctor takes a small sample of tissue from the uterine lining. This can be taken in OPD through a small tool, or by Dilatation and Currettage under anesthesia. Another doctor will look at the sample under a microscope to see if cancer is present.
Imaging
MRI pelvis with Upper Abdominal screening and Chest Xray are done to know the extent of the disease. It defines how much of the uterus is involved. It also tells us if there is spread of cancer outside the uterus.
CECT can be done if MRI is not available or patient cannot get that done. PET scan is done only in few cases in which there is a doubt of advanced disease.
Cancer staging is a way in which doctors find out how far the cancer has spread.
The right treatment for you will depend a lot on the stage of your cancer and how fast it is growing. Your treatment will also depend on your age and other medical problems.
Surgery
Extended Nelson`s Hysterectomy with Bilateral Salpingo oophorectomy is done. The lymph nodes into which cancer can spread next are also removed. Omental biopsy, fluid cytology and para aortic lymph node biopsy are taken to stage the disease. All these organs are checked for histopathology. Microscopic check of these tissues gives us the final stage. Subsequent treatment is decided according to this stage.
This surgery can be done by three methods
- Open Surgery
This is the conventional surgery in which incision is made and surgery is performed. - Laparoscopic Surgery
- Robotic Surgery
In Robotic Radical Hysterectomy, whole surgery is completed through 5 small holes. This is a Minimally Invasive Surgery, in which Extended Nelson`s Hysterectomy is done with robotic Assistance. It helps in early recovery and minimal blood loss. Fore more information, read Robotic surgery. - Radiation therapy – Radiation kills cancer cells. Radiation can be given from a machine that is outside the body. Or a doctor can put a source of radiation directly into the vagina.
- Chemotherapy – Chemotherapy is the medical term for medicines that kill cancer cells or stop them from growing. It is added in few cases which are advanced or aggressive.